FireCAD : Grate Fired Boiler Design Software
Grate Fired Steam Boiler (Stoker Fired)
Steam Generators Design Software Features:
- Solid fuel fired Steam Generators upto 200,000 Kg/hr and 550 degC can be designed.
(440,000 Lb/hr and 1022 degF) - Fuels : Coal fired boilers, bagasse boilers, Rice husk boilers, husk boilers, wood boiler,other Bio-mass boilers, Lignite boiler and other industrial steam Generators.
- Grates : Dumping Grate, Travelling Grate, Water Cooled Grates
- Furnace : Membrane tubes, Tangent Tubes, Space Tubes or Refractory wall
- SuperHeater : Single Stage and Two stage. Counter and Parallel flow type with or without protective screen.
- Boiler Bank: Water Tube or Fire Tube boiler Bank. Combination Boilers or Combi boilers with water tube furnace and Fire Tube Boiler bank.
- Water Tube boiler Bank : Cross Flow or Long Flow type.
- Fire Tube Boiler : Single Pass or Two Pass.
- Economizer: Single pass or Multi pass with Bare/Fin/Gill tubes.
- Air Heater: Single or Multi Pass.
- Headers, Downcomers , Feeders and Risers sizing
- complete system with Furnace,Boiler Bank, SuperHeater, Economizer and Air Heater.
General Features across all FireCAD software:
- Optimum design with AutoDesign feature
- Extensive Fuel database.
- Custom Fuels can be added to database
- Extensive help giving Design methodologies, Design tips and Good Engineering practices
- Detailed report of the final design with Print option
- Water/Steam/Gas properties,Combustion/Heat Transfer/Pressure drop calculations
- MKS/SI/FPS units supported

Brief Description of Grate Fired boilers
About:
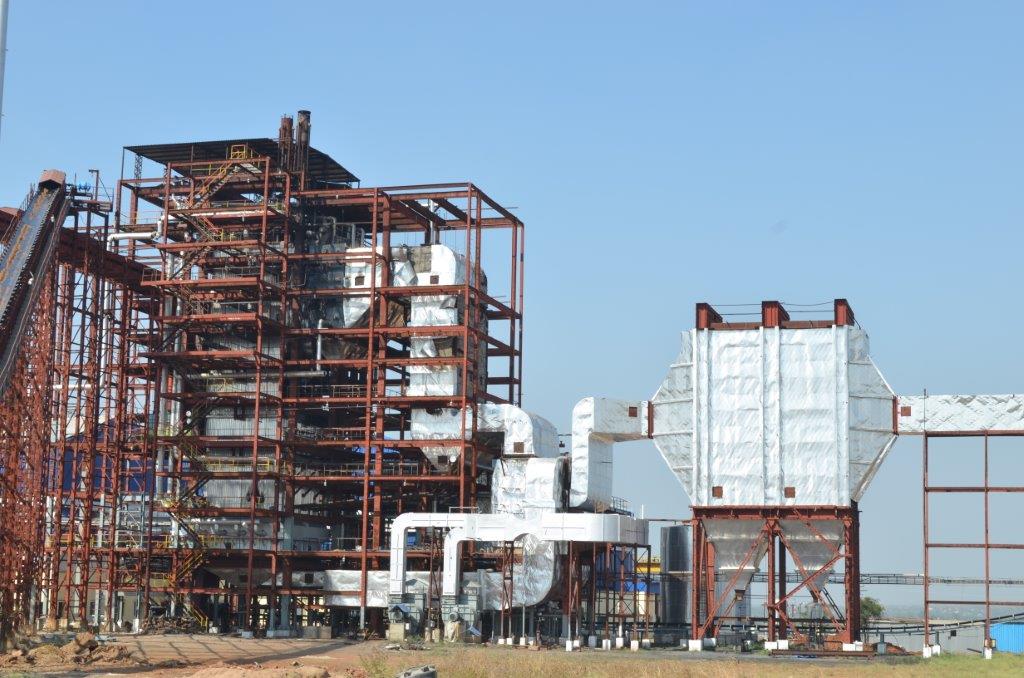
As the name indicates, Grate fired boilers or Grate Fired steam Generators are those boilers where the solid fuels are fired on grate. The grates can be inside the furnace or outside (external furnace boilers). These boilers are also called as Stoker fired boilers. They operate under balanced draft and furnace is maintained at slightly negative pressure.
Configuration
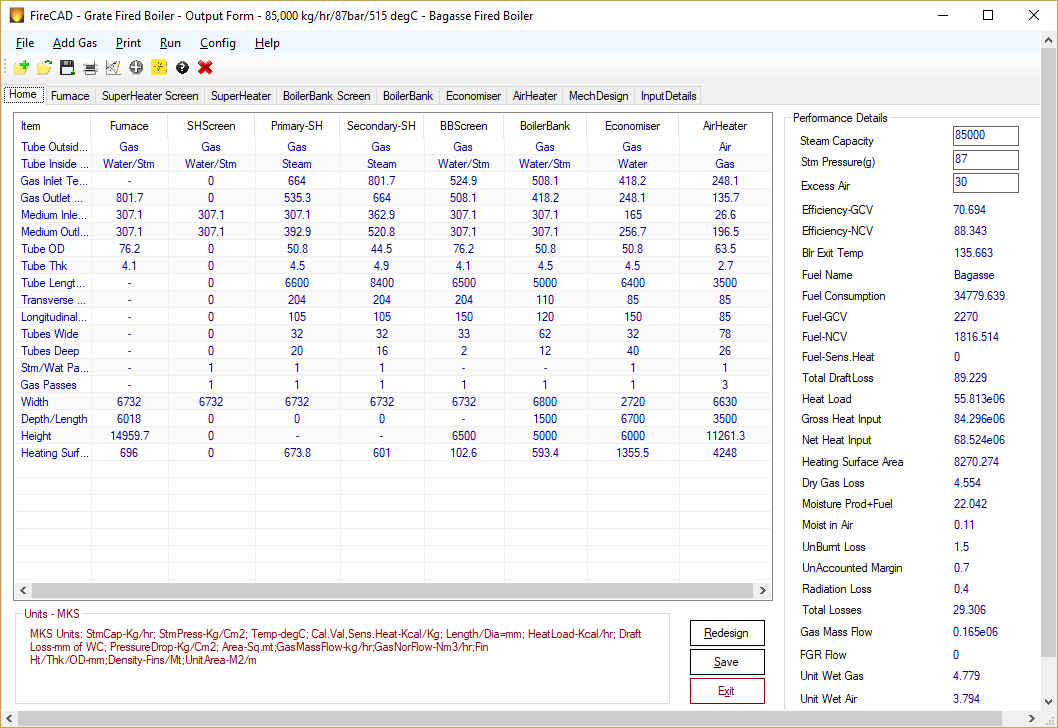
The steam Generator mainly consists of furnace, superheater, boiler bank, economizer and air heater. These boilers are water tube type except in combination boilers where the boiler bank is fire tube and the rest water tube.
Grate
Solid fuels like Coal or Bio-mass is fed into furnace with the help of mechanical or pneumatic fuel feeders and spreaders. Fuel burns on firing grate generating heat. Some of the fuel is burnt as soon as it enters the furnace in air and is called suspension firing. This heat is absorbed by various boiler heat transfer sections and used to convert water into steam. Depending up on the fuel type and it’s characteristics, a suitable grate is selected for firing purpose. There are various types of Grates available like Travelling grate, chain grate, inclined water cooled grate, pin hole grate, dumping grate, fixed grate ..etc. Travelling Grate is widely used for high ash content fuels and medium range boilers. Dumping grate is widely used for low/medium capacity boilers and low ash content fuels like Bagasse.
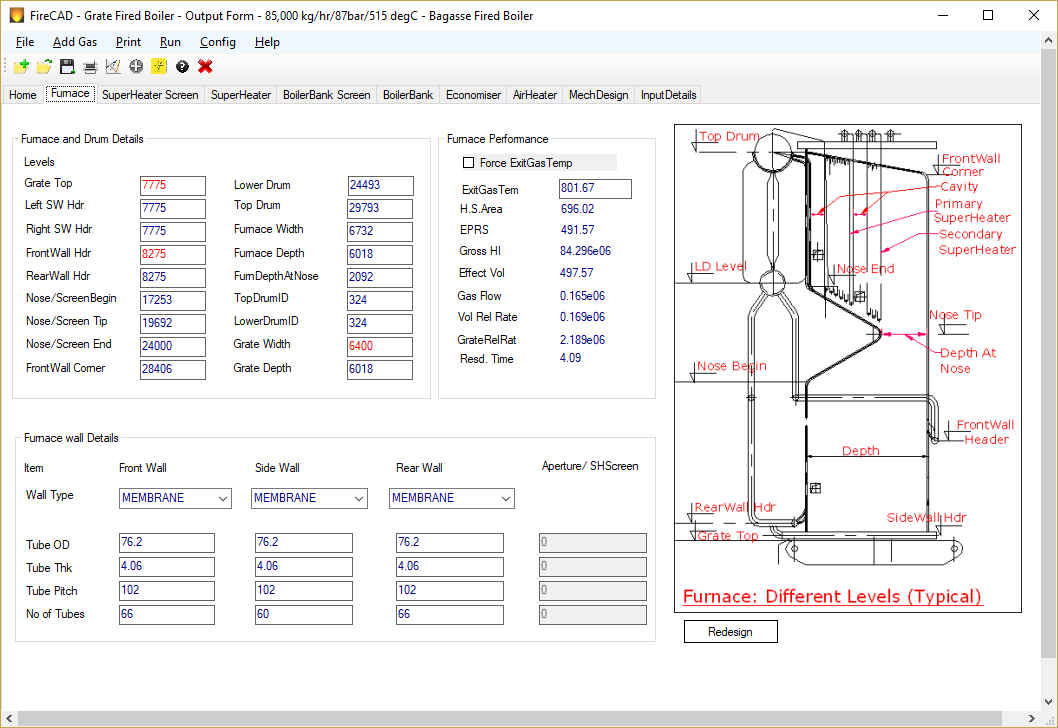
Furnace:
Furnace is usually vertical and water tube type. Furnace water walls are either membrane wall type or tangent tube wall or space tube type. Furnace absorbs major portion of the heat generated during fuel combustion through radiation heat transfer. Proper residence time is selected during furnace design in order to ensure that the fuel gets enough time to burn completely inside the furnace. Boiler furnace parts include furnace bottom headers and top headers on four walls connected with furnace wall tubes which absorb radiation in the furnace. Headers are usually made up of carbon steel pipes and tubes are also of carbon steel. Furnace has a provision for secondary air, fuel feeders. Furnace headers are connected to down comer pipes from Lower drum (water drum). Furnace top headers are connected to Steam/water drum or Top drum with the help of riser tubes/pipes thus completing the circuit. So water from lower drum enters the furnace lower headers and then passes through furnace tubes absorbing heat. Part of the water converts to steam on account of heat absorption and this two phase water/steam enters furnace top headers. This steam and water mixture then enters Steam Drum through risers thus completing the circuit. This process is called circulation and the term to describe this water to steam ratio is called circulation ratio. In water tube boiler furnaces this ratio ranges from 15 to 25 in the case of natural circulation boilers. In assisted circulation or forced circulation boilers, steam water mixture is circulated with the help of a pump unlike natural circulation boiler where it happens because of density difference between steam and water. So forced circulation is required for only high pressure boilers above 150 bar or so and the circulation ratio is much lower and less than 10. In single drum boilers, the furnace is made very tall to absorb the additional heat load required because of the absence of the boiler bank.
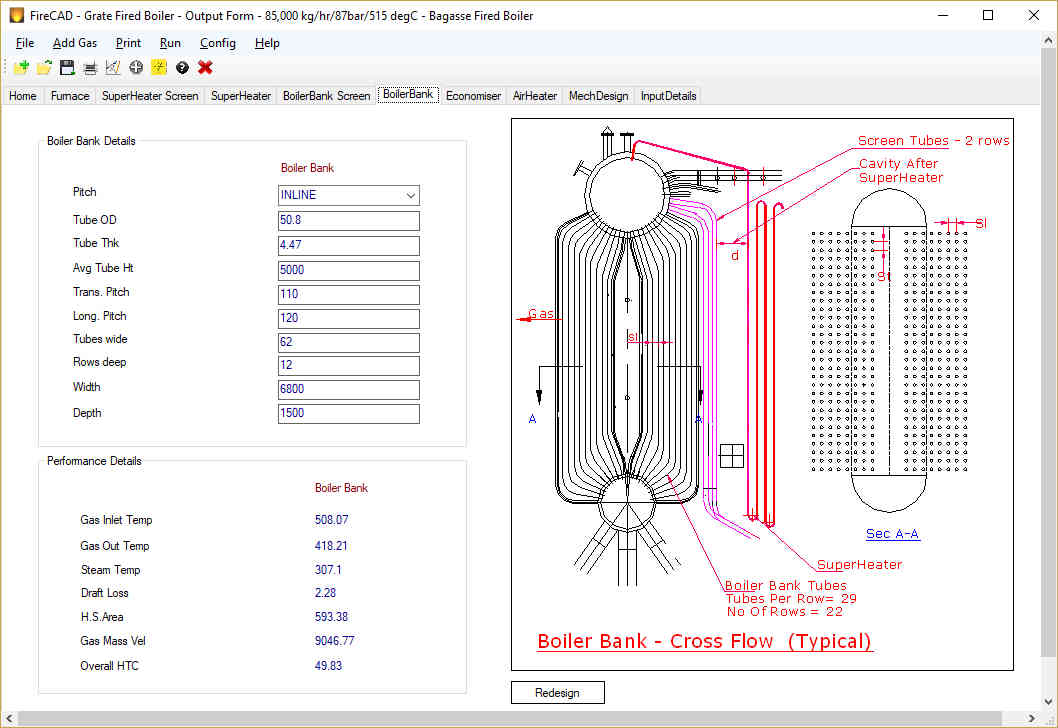
Boiler Bank:
Boiler bank absorbs heat from hot gases through convection. Usually Boiler bank is bulky as it has to absorb heat by convection at relatively low temperature. Most of the grate fired boilers are of Bi-Drum construction where the lower drum is always filled with the water and the upper drum is half full with water and the rest with steam. Both the drum are connected by hundreds of tubes and sometimes thousands of tubes. Material of construction is carbon steel for both the drums and tubes. Now-a-days single drum boilers are gaining popularity as this expensive boiler bank can be avoided. Rotary soot blowers are provided to dust-off the soot.
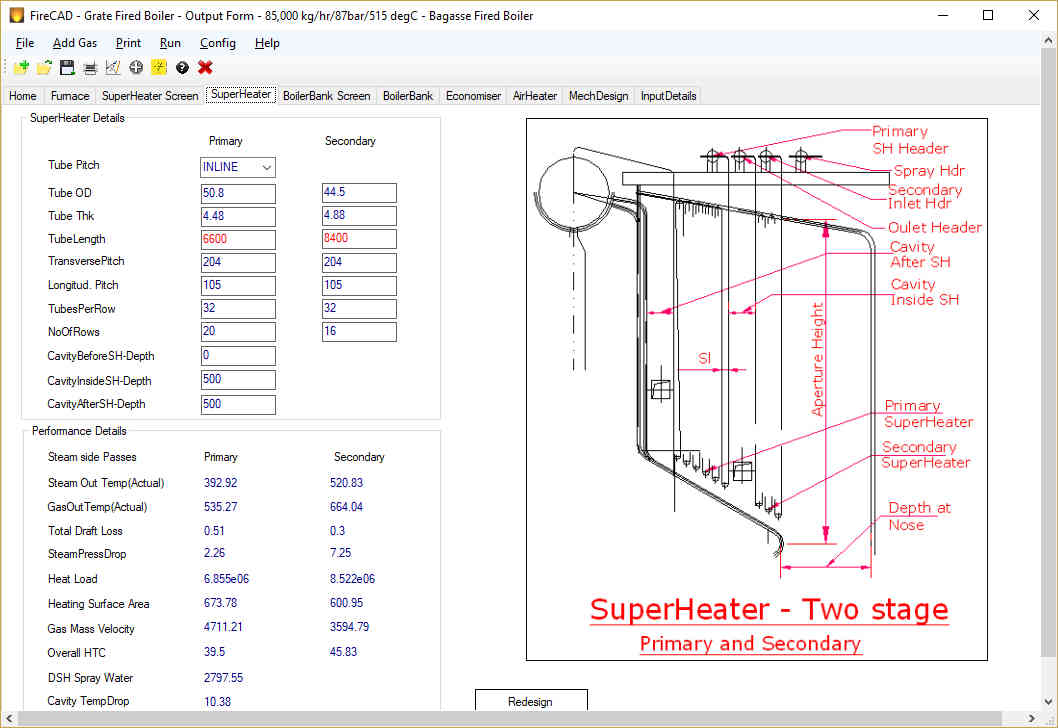
Superheater
Superheater is the prime section in any boiler. Right design of the superheater is very critical in the boiler. Superheater absorbs heat by direct radiation from furnace, by non-luminous radiation and by convection. Superheater section is generally protected by furnace nose in many industrial boilers. some superheaters, called platten type, kept directly hanging in the furnace to absorb more heat. Superheater consists of Inlet outlet headers connected with superheater coils. Inter-stage desuperheater / attemparetor is generally provided to control the steam outlet temperature. Depending up on the steam temperature and resultant metal temperature of the superheater coils either carbon steel or low alloy material is used. Superheaters are also provided with steam or sonic soot soot blowers of retractable type.
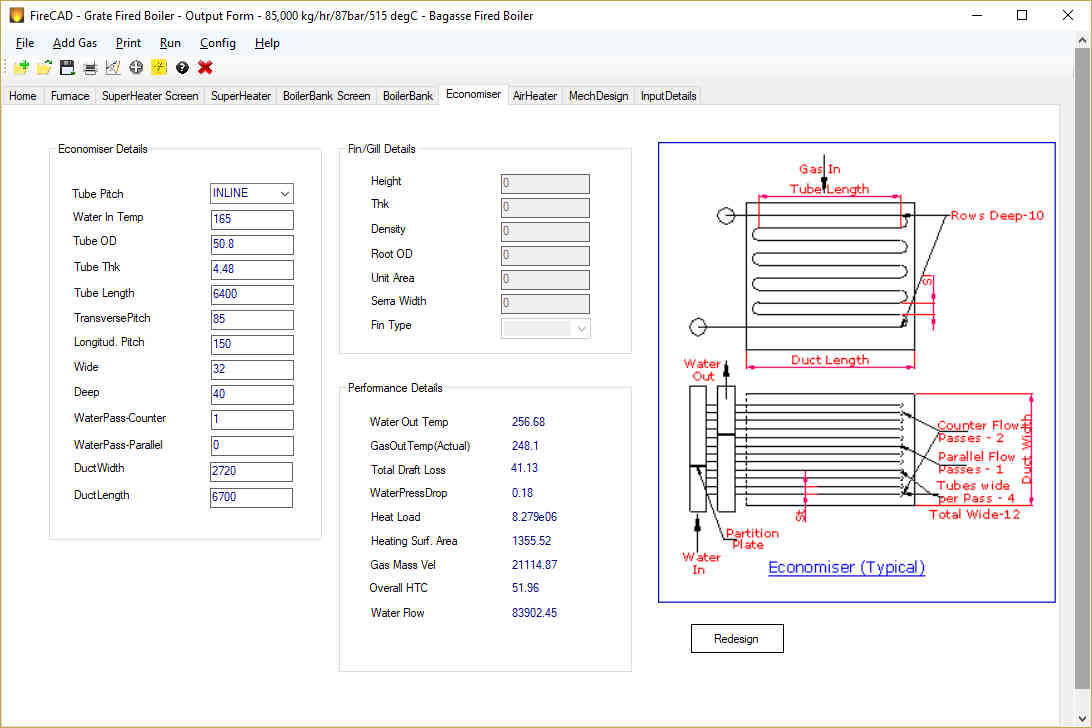
Economizer
Economizer is used downstream of Boiler bank to preheat the feed water absorbing heat from hot exhaust gases. Economizers are always water tube type. Bare tubes in Economisers are widely used in Industrial boilers and in some applications like Heat recovery boilers in Sulfuric acid plants, Gilled tubes are employed. Finned tubes are popular in HRSG applications. Economizers are retrofitted to many old boilers to increase the fuel efficiency of the boiler. Feed water can be heated up to a level about 20 – 30 C below saturation temperature of the boiler. Economizers need hot water input to reduce condensation of corrosive gases like SO2 on tubes. Depending up on the sulfur content in the fuel, water inlet temperature of 80 C up to 150 C is required for economizers.
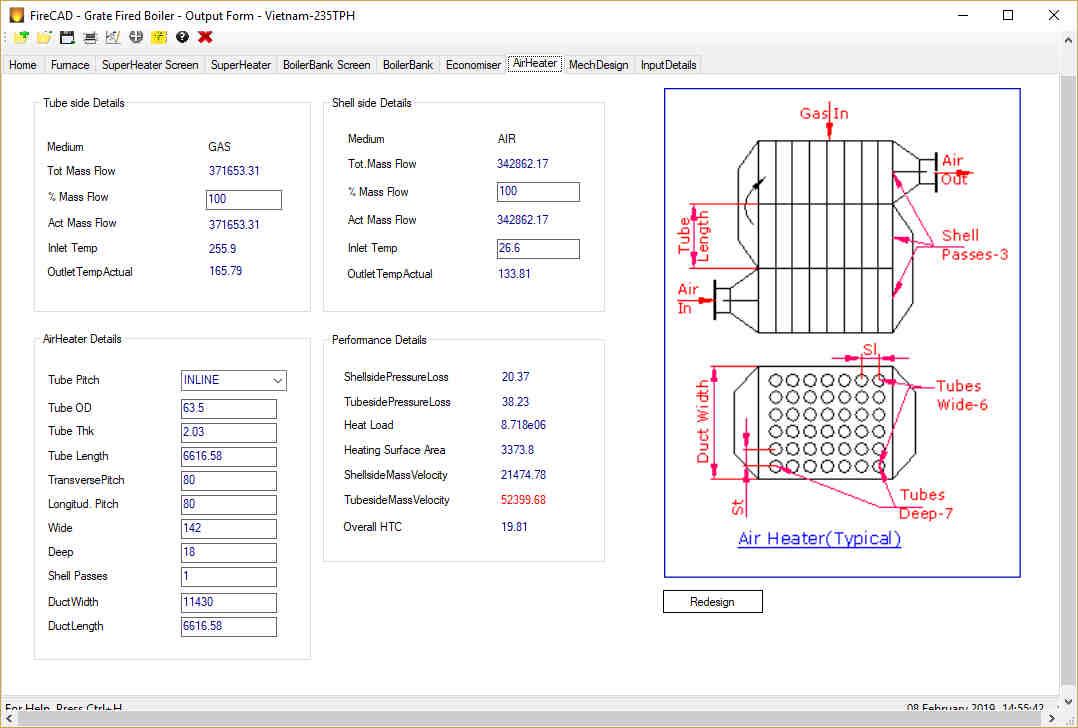
Air Heater
Air heater is used to preheat the combustion air before sending it to furnace for combustion. This also recovers heat from the exhaust gases and reduce the boiler outlet gas temperatures to a level of 130 to 170 C. Hot air helps combustion and hot air temperatures of 150 to 220 c are common in many industrial boilers. Hot air temperature is especially important, if fuel contains inherent moisture, like bagasse.
Boiler Parts
Boiler parts include boiler sections like furnace,superheater,boiler bank,economizer,airheater, steam and water drums. Fuel feeding section includes fuel storage, fuel bunker or silo, rotary,reciprocating or pnuematic fuel feeder, grate and ash discharge chutes.